
Simply saying that everything is connected doesn’t get you very far, though. The real challenge is to understand how. Most of the root causes of inequality and poverty relate to global rather than national dynamics. In the most practical and important sense, there is one global economic system. There are networks of national systems within it, but they are all part of, and increasingly subservient to, a single, mother system.
You don’t have to work from this perspective for long to recognize that there is a single set of rules governing this global economic system. They may be implemented in different ways or clothed in different language, but they are as true for the United States and Greece as they are for China and South Africa.
It’s important to realize that this global system, with its single set of rules, is actively being governed. There are people who see its wholeness clearly and operate from that perspective. Right now, most of these people, unsurprisingly, sit in organizations that have genuine planetary reach — private corporations, international institutions like the World Bank and the World Economic Forum, and a small number of large nongovernmental organizations. Unsurprisingly, the people with the most power in the global economy are those who align with its interests: They maintain their power by effectively promoting and implementing the rules of the status quo.
This isn’t some conspiracy theory, merely a truth about the nature of complex adaptive systems. The top priority of any system is to survive. Once a network becomes sufficiently complex, it becomes self-organizing. From that point on, it will always “want” to survive. One way the global economic system does this is to draw into positions of influence those people who best serve that purpose. A capitalist system, whose prime directive is the production of capital, will work constantly to refine and improve its ability to do just that. It will continue until it is stopped by an external force of some kind, or it collapses under its own weight. Unless a politically significant mass of people actively chooses otherwise, the rules of the system will govern us, not the other way round. If the rules are to be changed, we cannot expect the system to autocorrect. We must change them manually.
Challenging the Truism That “Growth Is Good”
There are few rules of the single global economy more fundamental than its prioritization of growth. The mantra that “growth is good” has been repeated so often that it has the feel of common sense. It is almost impossible to think of how economies might work, let alone how inequality and poverty might be reduced, if we aren’t growing the amount of capital there is in the world through ever-increasing production and consumption.
This logic pervades all international debates and plans. Take, for example, the recent “Sustainable Development Goals.” They rest on the fundamental assumption that every country, every company and even every human being must grow their material wealth over time, as a precondition to anything else. This is measured in GDP for countries, and profit for businesses. In other words, they obey the rule that the global economy must grow continually through the perpetual growth of all of its parts.
But what if there is a fatal flaw in this logic? What if this rule is not fit for the purpose of guiding us into the future? What if, instead of being a panacea for all that is good, it is a driver of so much that is bad?
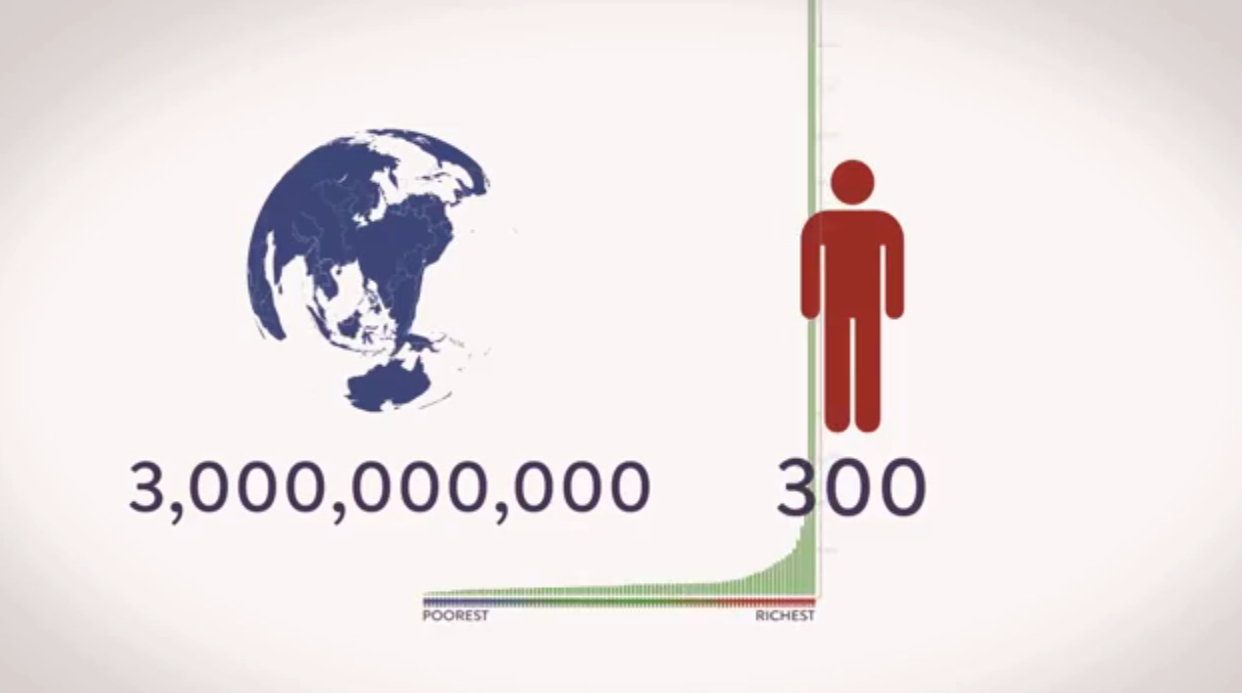
The evidence is clear. Totalitarian growth of all parts of the system has not only led to destabilizing the climate by making sure consumption is always increasing, everywhere, but has also created vast amounts of poverty and inequality. This might sound counterintuitive at first glance — doesn’t more money mean less poverty? But consider this: Since 1990, global GDP has increased 271 percent, and yet both the number of people living on less than $5 a day, and the number of people going hungry has also increased, by 10 percent and 9 percent, respectively. Add to that the wage stagnation across wealthy nations, and increasing inequality both within and between countries pretty much everywhere, and the shakiness of this basic logic becomes evident. Aggregate economic growth does not translate into less poverty.
Maybe this would only be problematic, something that could be fixed by tweaking the growth model while keeping the basic imperative in place, were it not for the second part of the problem. The imperative for every part of the system to constantly grow its material wealth is destroying us, in the most real and painful way. The consumption-driven mechanisms we use to achieve it, and the GDP measure we use to define it, have us locked on a path to ruin by actively encouraging us to treat finite natural resources as if they were infinite, and prioritize the growth of the money supply over everything else. Said another way, the perceived moral imperative for economic growth actually contradicts the laws of nature.
Connecting the Dots
It is only by connecting dots that we start to be able to see the true shape of the challenges we all face. Whatever our issue-focus, there are underlying rules and norms that affect every facet of human life. Growth is just one.
At first glance, connecting dots in this way might make the job of radical change feel more difficult. We struggle hard enough to affect change locally, let alone nationally, let alone globally. But something liberating and empowering happens when you start to connect the dots to see what’s going wrong; the same process also allows you to connect the dots between the struggles for making things better. We start to see that what’s driving the destruction of the rainforest in Indonesia is the same basic set of rules that are causing rising food prices in Kenya, and the explosion of student debt in the United States. We become connected, in very real and actionable ways, by a realization that we are all being screwed by the same basic set of rules.
Most importantly, we start to see new and different solutions. Ideas that previously seemed to only mitigate one problem can start to be seen to mitigate all.
For example, strong local economies with independent currencies and food sovereignty challenge the monoculture model of “development.” Gift economies that deny the commodification of life disrupt the system’s rules by their very existence. As we contract new types of relationships, with each other, with our communities, with nature itself, we will usher in new types of social relations based on a vast range of diverse and mutually supporting solutions that will render the old paradigm, with its slavish adherence to ideas like perpetual growth, wholly obsolete.
These new models and experiments are already taking place all around us. From the Brixton pound in Britain, to the Zapatistas in Mexico, to Rojava, the Kurdish free state in northern Syria, a new breed of post-capitalist thinking is taking hold and spreading through networks of conscious people. However, the mainstream media is not set up to see these shifts. They are pushing the old story of growth, lifting boats, charity and “financial access.” And in their blindness lies our opportunity. The antidote lies in our ability to see how the old system is connected, while recognizing the patterns in the diversity and wellspring of wonder and power that is filling the void of the crumbling edifice of growth-based capitalism. The question is, will we connect the dots before it’s too late?
Photo credit: DryRot via Visualhunt / CC BY-NC-ND








Local currencies are good, but I have an idea for a slightly evolved version of an alternative currency that is based on giving the seller an ability to set price in “hours of your personal time”. A price tag is usually written as a mix of dollars and hours such as “1hr + $1”. For something like a digital download, the $1 covers the fixed overhead cost of delivering one additional digital download. The 1hr is multiplied by how much an hour of your time is worth/cost convert it to a dollar amount. For example if you make $10/hr then your cost for the download is $11 = (1hr X $10/hr + $1). If you are in the 1% and your time is worth $1000/hr then your cost of the download is $1001 = (1hr X $1000/hr + $1). This pricing strategy makes the seller a lot of money compared to regular dollar only pricing. And, as a side effect (from the sellers perspective), it reduces poverty a lot by the method of differential pricing advantages giving only to poor people and in proportion to how poor they are.
interested in reading more https://www.facebook.com/hOursEqualsPrice